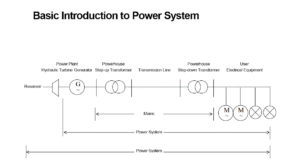
Bloga
What Is a Servo Motor Explained with Types Features and Uses
How Servo Motors Work
At the heart of a servo motor is a układ sterowania w zamkniętej pętli that continuously adjusts its position based on feedback. Unlike regular motors that just spin when powered, servo motors know exactly where they are and move precisely to the desired angle or position.
Core Working Principle: Closed-Loop Control with Feedback
A servo motor operates using a feedback mechanism that makes real-time corrections to its position. This system compares the target position (the command) with the actual position detected by a sensor inside the motor. If there’s any difference, the motor adjusts accordingly until the two match perfectly.
What is PWM (Modulacja szerokości impulsu)?
The control signal for the motor’s position is sent using PWM (Modulacja szerokości impulsu). PWM controls the servo by sending pulses of varying widths at a fixed frequency. The length of each pulse tells the motor what angle to turn to:
- Short pulses signal one end of the range
- Medium pulses center the servo
- Long pulses command the opposite end
Step-by-Step Process
- Command Signal: A controller (like an Arduino) sends a PWM signal commanding a specific position.
- Controller Inside the Servo: Converts this signal into motor movement instructions.
- Motor Adjustment: The motor begins turning the output shaft to the commanded angle.
- Feedback Correction: A feedback sensor (usually a potentiometer) measures the shaft’s position and sends this info back to the controller. If the position isn’t correct, further adjustments are made.
Proportional Control for Smooth Operation
Many servos use a proportional control system where the motor’s speed depends on how far it is from the target position. This means the motor moves quickly when far away and slows down as it approaches the desired angle. The result is smooth, precise, and efficient movement without overshooting or jerking.
In short, servo motors work by constantly comparing a command signal to the motor’s actual position and making precise corrections through PWM, ensuring accurate and fast responses every time.
Key Components of a Servo Motor
A servo motor is made up of several essential parts that work together to provide precise control and movement. Here’s a quick breakdown of the key components:
- DC Motor (or AC Motor in industrial models): This is the main drive unit that generates rotational force. Hobby and small servos typically use DC motors, while industrial servo motors often use more powerful AC versions for higher performance.
- Gearbox: Attached to the motor, the gearbox reduces speed and boosts torque, giving the servo the strength it needs to move loads accurately.
- Position Feedback Sensor: This component keeps track of the motor’s current position. In hobby servo motors, a potentiometer is used, which sends a variable resistance signal based on shaft position. Advanced models use encoders that provide more precise feedback.
- Control Circuit Board: It processes the input commands and compares the feedback signal to adjust the motor’s position accordingly. This circuit handles the closed-loop control crucial for smooth and responsive operation.
- Output Shaft and Horn: The shaft connects to servo horns or arms, which transfer the motor’s motion into physical movement for the project or machine.
Understanding these parts can help you know why servo motors are so effective for tasks requiring high precision and reliability. If you’re looking into industrial applications, combining servo motors with modern control systems, like those discussed in reliable VFD and PLC integration solutions, can further enhance performance.
Rodzaje serwomotorów
Servo motors come in several types, each tailored for different applications. The most common is the positional rotation servo, which typically moves within a limited range, usually 90° or 180°. These are widely used in hobby projects where precise angle control is needed.
Another popular type is the continuous rotation servo, which can rotate endlessly in either direction. These servos are great for driving wheels or conveyor belts where full rotation is necessary, but without specific position feedback.
Linear servo motors offer straight-line motion instead of rotation, useful for applications that require pushing or pulling.
When it comes to the power source, DC servo motors are common in early hobby and many industrial setups, while Serwosilniki prądu przemiennego are often found in more demanding industrial environments due to their higher efficiency and torque.
A special mention goes to mini servo motors, like the popular 9g micro servo SG90. These tiny units are perfect for small-scale projects like lightweight robots, model airplanes, and Arduino-based devices that require compact, precise motion control.
For those interested in industrial-grade options, high-quality CNC components often include specialized servo motors designed for precision automation.
Whether you need a standard positional servo or a tiny micro servo, understanding these types helps select the right motor for your project’s needs.
Servo Motor Drivers and Control

servo motor driver pwm control basics
A servo motor driver is a vital component that controls the power and signals sent to the servo motor. It acts as the bridge between your microcontroller (like an Arduino) and the motor itself, ensuring accurate movement by managing the motor’s position, prędkość, i moment obrotowy.
Most servo motors are controlled using PWM (Modulacja szerokości impulsu) signals, which tell the servo how far to rotate by adjusting the signal’s pulse width. For beginners working with Arduino or other microcontrollers, PWM control is straightforward: you send a pulse corresponding to the desired angle, typically between 1ms and 2ms in length, repeated every 20ms.
Here are some quick tips for wiring and setup:
- Connect the servo’s power and ground lines to a stable power source, usually 5V for mini servo motors like the popular 9g micro servos.
- Connect the control wire to a PWM-capable pin on your microcontroller.
- Use a separate power supply for the servo if it draws more current than your microcontroller can safely provide.
Common servo drivers range from simple signal buffers for hobby servos to more advanced integrated circuits in industrial applications. If you’re stepping into industrial automation or CNC control, products such as Fanuc servo drivers provide precise control and reliability.
Understanding the right driver and control method will help you get the most out of your servo motor, whether it’s a small hobby servo or a powerful industrial unit.
Zalety i wady serwomotorów
Servo motors offer high precision I efficient performance, making them ideal for applications that need accurate positioning and quick responses. They provide strong holding torque, which means they can maintain a position under load without slipping—a feature that simple motors often lack. Plus, their fast reaction times allow for smooth and precise control in robotics, Maszyny CNC, and drone stabilization.
Jednakże, these benefits come at a price. Servo motors tend to be more expensive than regular DC or stepper motors. Their design is more complex since they rely on closed-loop control systems with feedback sensors, which also means more potential points of failure and maintenance needs. Additionally, servo motors generally consume more power, especially when holding load or running continuously, which might be a drawback for battery-powered or low-energy projects.
Balancing these factors will help determine if a servo motor fits your specific needs, whether for hobby projects or industrial applications. For quality and reliability in mini servos, options like DUOMI mini servo motors are worth exploring.
Typowe zastosowania serwomotorów
Servo motors are everywhere, from your weekend projects to high-end industrial machines. Here’s how they shine in various fields:
Hobby and DIY:
- RC cars, samoloty, and drones rely on mini servo motors for precise control of steering, przepustnica, and flaps.
- Arduino robotics projects use servos for smooth, accurate movement, making them a favorite among hobbyists.
Industrial Applications:
- Precision is key in CNC machines and automation lines, where Serwosilniki prądu przemiennego and DC servo motors manage tooling and positioning tasks.
- Conveyor systems benefit from servo motor drivers that ensure smooth, reliable operation.
Other Uses:
- Camera gimbals use servo motors for stable image capture, compensating for movement on the fly.
- Prosthetics incorporate small servo motors to mimic natural joint motions.
- Antenna positioning systems use servos for accurate alignment, crucial in communication setups.
These diverse applications prove why servo motors are so valuable—combining precision, reliability, and versatility makes them ideal for both simple and complex motion control tasks.
Choosing the Right Servo Motor
Picking the right servo motor depends on several key factors to match your project’s needs. Here’s what to consider:
- Torque rating (kg-cm): Make sure the servo’s torque fits the load you need to move. Higher torque means more power to handle heavier or more resistant parts.
- Size and weight: For compact projects or drones, mini servo motors are ideal since they’re lightweight and small.
- Woltaż: Check the voltage requirements to ensure compatibility with your power supply or controller.
- Prędkość: The servo’s speed affects how fast it responds—important for dynamic applications like robotic arms or RC cars.
- Gear type: Plastic gears are common in hobby servos for cost-effectiveness, but metal gears offer better durability and strength for heavy-duty use.
For small projects, mini servos like the popular 9g micro servo are a solid choice. They balance performance with compact size and work well in Arduino robotics, DIY drones, and RC vehicles.
If you’re after a reliable mini servo, consider high-quality options like DUOMI mini servo motors. These provide consistent torque, smooth operation, and durability—perfect if you want to avoid common issues like jitter or premature wear. Check out DUOMI’s selection for dependable small servo motors that work well in a variety of applications.
For advanced control setups, make sure you pair your servo with a compatible servo motor driver to optimize performance and protection. You can find useful servo drivers like this Siemens SIMATIC MP Touch Panel for automation projects that demand precision and ease of use.
Choosing the right servo will make your project smoother, smarter, and more reliable — whether you’re building a hobby robot or an industrial automation system.
Frequently Asked Questions about Servo Motors
What makes a servo different from a stepper motor?
A servo motor uses a closed-loop control system with feedback to reach and hold a specific position accurately, while a stepper motor moves in fixed steps without feedback. Servos adjust position smoothly with proportional control, making them better for precise and responsive tasks compared to the open-loop, stepwise motion of stepper motors.
How to control a mini servo with Arduino?
Controlling a mini servo, like the popular 9g micro servo, involves sending PWM (Modulacja szerokości impulsu) signals from the Arduino to the servo’s signal wire. Arduino’s Servo library simplifies this by letting you set angles directly in code, usually between 0° to 180°. Just connect power, ground, and the signal pin to your microcontroller, and you’re ready to move the servo easily.
Can servo motors run continuously?
Standard positional servos are designed for limited rotation (usually up to 180°) and aren’t built for continuous spin. Jednakże, continuous rotation servos modify the feedback mechanism to allow endless rotation, acting more like a motor with speed control. These are popular for robots needing wheel movement or continuous motion.
Troubleshooting common issues: jitter, overheating
- Jitter: Often caused by weak power supply, poor grounding, or noisy PWM signals. Use a stable power source and shielded wiring to reduce interference.
- Overheating: Can result from overloading the servo beyond its torque rating or continuous stalling. To prevent damage, choose the right servo for your load and avoid long periods of stall under high torque.
- Również, check connections and controller settings to ensure proper signal timing and no interference.
For those looking for reliable servo options or specialized servo motor drivers, check out quality models and controllers that ensure smooth performance throughout your projects. High-quality mini servos and industrial-grade drivers can be found through detailed resources like this collection of servo motor drivers and amplifiers.