Blogue
8 Tips for Troubleshooting Servo Motor Problems Fast and Easy
If your servomoteur is acting up—whether it’s not moving, jittering, or throwing alarms—every second of downtime costs you money. The good news? Most common servo motor problems are easy to pinpoint and fix if you follow the right steps. Dans ce guide, you’ll get 8 tips for troubleshooting servo motor problems that work across brands like Doumi, Yaskawa, Mitsubishi, and Siemens. No fluff, no theory—just fast, practical, step-by-step actions you can take right in your workshop to find and solve issues quickly. Stick to this checklist, and you’ll eliminate 90% of faults in under 30 minutes. Let’s dive in and get your servo back on track.
Verify Power Supply Stability First
Power problems are the most common cause of servo motor not moving or erratic behavior. Start by checking your power supply—if it’s unstable, everything else falls apart.
Watch for these power-related symptoms:
- Servo jittering or random stopping
- Frequent servo drive alarm codes without clear cause
- Motor humming but not turning
- Unexpected resets or shutdowns
Make sure to check the voltage levels carefully. Measure main power voltage et 24 VDC or 48 VDC control power separately—they serve different functions and need their own verification.
How to properly check power with your equipment:
- Use a multimeter to verify DC voltage levels are within specs.
- For ripple or noise, use an oscilloscope to spot voltage fluctuations that a multimeter can’t catch.
- Test under load as ripple and drops may only show up when the motor is running.
Common mistake: Don’t confuse main power (the high voltage driving the motor) avec logic power (the low voltage powering the drive/control board). Both must be stable, but checking the wrong one can lead you down the wrong path.
By confirming your power supply is stable and clean first, you’ll avoid wasting time hunting for phantom problems later. If you find any abnormalities, fix them before moving to the next troubleshooting step.
Inspect All Wiring and Connections (Le #1 Cause of Failures)
Wiring and connections are the most common culprit when your servo motor is not moving or showing jitter. Start by checking for loose or oxidized cables—power lines, encoder feedback cables, and brake connections can all lose contact or degrade over time.
Don’t overlook shielding and proper grounding, either. Ground loops are a sneaky cause of servo jittering and erratic behavior. Make sure cable shields are connected properly and that grounding follows your system’s best practices.
A quick, safe test is to gently wiggle cables while the servo is powered on. If the motor jerks or alarms show up during this, you’ve found a suspect connection.
Enfin, tighten terminal blocks to the recommended torque values. Over-tightening can damage connectors, but under-tightening leads to looseness and failure. Proper torque ensures reliable contact throughout the system.
For more on wiring best practices and motor control essentials, check out this industrial automation resource from Doumi.
Look for Overheating and Thermal Shutdown
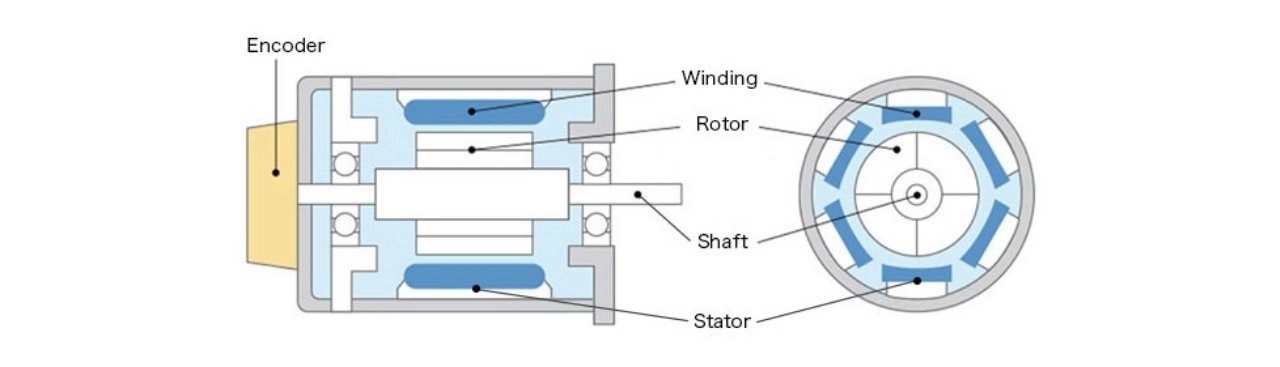
Overheating is a common cause of servo motor problems, often leading to thermal shutdowns that stop your system unexpectedly. Knowing the normal temperature range for your motor is key—typically, the motor should run cooler than 80°C (176°F). Temperatures above this range can signal trouble, especially if it triggers alarms or trips the thermal protection.
Start by cleaning heatsinks and ensuring cooling fans are running smoothly. Dust buildup or a failed fan can drastically reduce cooling efficiency. If your motor operates in a hot environment—above 40°C (104°F)—you need to derate the motor’s load capacity to avoid overheating. This derating prevents premature thermal shutdown and extends motor life.
Aussi, familiarize yourself with your drive’s thermal error codes. These codes help pinpoint whether the fault comes from the motor winding, the drive itself, or external conditions affecting heat buildup. By monitoring these conditions closely, you can prevent overheating issues before they cause serious damage.
For more technical insights on drive systems that handle thermal management efficiently, check out high-quality options like the Delta Drive ASD-A2 series.
Check the Feedback Device (Encoder or Resolver)
Most intermittent servo motor problems stem from encoder failures. If you notice symptoms like position drift, following errors, or alarms labeled A, C, or E on your servo drive, the feedback device is often the culprit. These errors can disrupt precise motor control and cause jitter or unexpected stoppages.
For absolute encoders, make sure the battery backup voltage is stable—if the battery is weak or dead, the encoder might lose its position reference on power loss, leading to errors at startup.
A quick way to test the encoder is by using the drive’s diagnostic screen. This tool helps verify feedback signal quality and checks for any irregularities without needing extra equipment.
If you use products like the Siemens 3SU1500 series components, ensure the encoder wiring matches specifications to avoid common failures. For detailed troubleshooting, you might also want to look into compatible ABB ACS550 drives, which feature built-in diagnostic functions tailored for feedback devices.
Review and Reset Controller & Drive Parameters
Incorrect controller and drive settings are a common cause of servo motor issues like oscillation, no movement, or unstable operation. Key parameters to check include:
- Inertia Ratio: Mismatch can cause sluggish or jerky motion.
- Gain Settings: Improper tuning leads to servo jitter or hunting.
- Electronic Gear Ratio: Wrong values cause position errors or stalls.
Quick Parameter Backup Before Changes
Always back up current settings before making changes. Use the drive’s diagnostic tool or controller interface to export parameters to a file or memory. This lets you restore working values if needed.
| Common Parameter Issue | Symptom | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Inertia Ratio wrong | Overshoot, oscillation | Adjust based on motor and load |
| Gains too high/low | Servo jitter or slow response | Tune gains incrementally |
| Gear Ratio incorrect | No movement, position errors | Verify and correct gear ratio |
If your drive supports it, consult the controller’s manual or software for recommended default settings and reset procedures. For advanced troubleshooting, check alarm codes and parameter lists before resetting.
For more on controlling and troubleshooting automation devices, explore resources on contrôles d'automatisation industrielle.
Detect Mechanical Binding or Excessive Load
Mechanical binding or excessive load is a common cause of servo motor problems like jitter, stalling, or alarm triggers. Start by checking the coupling alignment—misaligned couplings can cause uneven load and damage to the motor shaft. Suivant, inspect belt tension; too tight or too loose belts strain the motor or slip, affecting performance. Don’t forget to look for bearing wear—damaged bearings can create resistance that feels like increased load.
To pinpoint the issue, measure the actual load on the motor and compare it to the motor’s rated torque. If the load exceeds the motor’s capacity, it can cause overload alarms or even damage the servo drive. Souviens-toi, un overload alarm means the motor is fighting too much mechanical resistance, while an overcurrent alarm indicates electrical issues like a short or a stalled rotor.
Keeping mechanical parts in good condition ensures smooth servo operation and fewer headaches troubleshooting issues.
Test Brake Operation (If Equipped)
If your servo motor hums but doesn’t turn, a common cause is the 24 V brake not releasing properly. This prevents the motor shaft from spinning even though power is applied.
How to Check and Manually Release the Brake:
- Listen for clicking sounds: When power is applied, you should hear the brake release.
- Manually release the brake: If safe, manually disengage the brake to see if the motor shaft moves freely.
- Measure coil resistance: Use a multimeter to check the brake coil’s resistance against the manufacturer’s specs. An open or short coil usually means the brake unit needs replacing.
Typical Brake Failure Modes:
- Coil burnout from overheating or overvoltage.
- Mechanical sticking due to worn friction material.
- Dirt or corrosion causing the brake to jam.
If the brake doesn’t release even after these checks, it’s likely time for a replacement. For more on reliable servo components, check out trusted Siemens automation parts that fit many servo systems.
Consider Environmental Factors and EMI

Environmental conditions can seriously affect your servo motor’s performance. Dust, oil mist, heavy vibration, and high humidity are common culprits that cause servo jittering or erratic behavior. These factors can degrade insulation, corrode connectors, and cause intermittent electrical faults over time.
Another big issue is electromagnetic interference (EMI), especially if your cables run too close to variable frequency drives (VFD), welding machines, or other noisy equipment. EMI can cause encoder feedback failure or random servo drive alarm codes that are tough to trace.
Here are quick fixes to minimize environmental and EMI problems:
- Use ferrite cores on signal and power cables to reduce high-frequency noise.
- Keep power cables and feedback cables separated to avoid cross-talk.
- Reroute cables away from VFDs or welding machinery whenever possible.
- Double-check that cable shields are properly grounded to prevent ground loops.
For more detailed info on minimizing VFD-related interference, check out our guide on VFD and PLC integration to keep your servo system running smoothly in demanding environments.
Bonus Fast-Check Checklist (Downloadable PDF Offered via Doumi Site)
To save you time troubleshooting servo motor problems, we’ve put together a fast-check checklist that covers the essentials. This handy PDF guides you through quick inspections, from power supply checks and wiring to feedback devices and mechanical issues. It’s perfect for technicians who want a clear, step-by-step aid to diagnose common faults and avoid the most frequent mistakes.
What’s included in the checklist?
- Verify stable power supply and correct voltage levels
- Inspect all wiring and connector conditions
- Identify signs of overheating and proper cooling
- Test encoder feedback integrity
- Review and reset controller parameters safely
- Detect mechanical binding or load problems
- Confirm brake function operation
- Spot environmental factors affecting performance
You can find the full checklist on the Doumi website, designed especially for U.S. users needing fast, reliable servo motor troubleshooting tips. Keep it handy on your mobile device or print it out to streamline your maintenance routines.
For more in-depth help with servo motor selections or diagnostics, check out Doumi’s range of products like the Heidenhain encoder or Mitsubishi servo motors, both trusted in the American manufacturing sector.
When to Call Doumi Technical Support
Sometimes, troubleshooting reaches a point where the issue is likely inside the servo motor or drive itself—think IGBT failure, motor winding damage, or internal component faults. At that stage, it’s best to call Doumi technical support for expert help.
When to Reach Out
- Persistent servo drive alarm codes that don’t clear after resets
- Moteur humming but not moving despite correct wiring and power
- Consistent encoder feedback failure after checking cables and parameters
- Overheating warnings not explained by external factors
- Mechanical checks done, but problem like servo jittering or following error remains
How to Collect Data Before Calling
Having the right info on hand speeds up diagnosis and repair. Prepare this before you call:
| Data Needed | Description | Why it Helps |
|---|---|---|
| Alarm Code | Exact error messages displayed | Pinpoints the faulty system part |
| Parameter List | Current motor and drive settings | Identifies incorrect gain tuning or inertia mismatch |
| Photos | Close-ups of wiring and setup | Check for visible loose connections or damage |
| Environmental Notes | Ambient conditions, recent changes | Rule out external causes like EMI or overheating |
| Test Results | Multimeter, oscilloscope readings | Confirms power supply stability or wiring problems |
Preparing these details ensures you get the most accurate support from Doumi technical experts, minimizing downtime and replacement costs.
For additional help with servo motors like the Mitsubishi HG-SR702B, you can check detailed product info and support options at the Mitsubishi HG-SR702B motor page.