Blogue
How to Install MKS SERVO42D NEMA 17 Servo Driver Controller Guide
Understanding the MKS SERVO42D: Why It Beats Standard Stepper Drivers
If you’re upgrading your NEMA 17 motor setup, le MKS SERVO42D servo driver controller is a game changer worth knowing. Unlike typical open-loop stepper drivers, this is a closed-loop system that brings precision, quiet operation, and reliability to your 3D printer or CNC machine.
Core Features and Tech Specs
- Closed-loop feedback through an encoder for zero missed steps.
- Supports up to 4.2A continuous current, plenty for most NEMA 17 moteurs.
- Compatible with FOC (Field-Oriented Control) algorithms for smooth torque delivery.
- Communication options include Pulse/Dir mode, RS485, and even CAN bus control.
- Compact design with onboard heatsink for stable thermal management.
- Encoder resolution support up to 8192 pulses per revolution (PPR).
Compatibility with NEMA 17 Motors and Firmware
This driver is tailor-made for NEMA 17 moteurs, especially those equipped with encoders, offering a substantial upgrade from basic stepper drivers. It plays nicely with popular firmware like Klipper et Marlin, both of which now support closed-loop configurations and allow you to easily switch between open-loop et closed-loop modes.
Pros and Cons Compared to Typical Drivers
Pros:
- Eliminates step skipping, leading to better print quality et quiet operation.
- Offers real-time torque and speed adjustments for smoother motion.
- Reduces motor heating dramatically due to efficient current use.
- Supports multiple control interfaces, increasing flexibility.
Cons:
- Slightly more complex to wire and configure compared to plug-and-play stepper drivers.
- Requires encoder installation and proper alignment.
- Typically costs more upfront, but the benefits often justify the investment.
When to Use Closed-Loop vs Open-Loop Modes
Closed-loop mode is your go-to when you want to prevent step losses during high-speed or torque-intensive prints. It’s ideal for precision applications and reducing printer noise. Open-loop mode is simpler and can save some setup hassle if your project has modest speed and torque needs, but you’ll sacrifice some performance.
Dans , the MKS SERVO42D steps up your motor control game by offering closed-loop reliability and advanced features that standard drivers just can’t match—especially when paired with popular firmware and a good NEMA 17 servomoteur. Ready to dive into installation? Let’s get hands-on next!
Preparation: Outils, Materials, and Safety Essentials
Before installing the MKS SERVO42D servo driver controller on your NEMA 17 motor, gathering the right tools and materials is key. Here’s what you’ll need:
Bill of Materials
- MKS SERVO42D driver controller
- NEMA 17 closed-loop stepper motor compatible with encoders
- Encoder magnet and mounting accessories
- Power supply matching your motor and driver requirements (typically 12-24V)
- Shielded cables for motor and encoder wiring
- Control interface cables (e.g., RS485, CAN bus, or step/direction wires)
- Connectors and terminals compatible with your hardware
Essential Tools
- Wire strippers and cutters
- Small Phillips and flathead screwdrivers
- Multimeter for voltage and continuity testing
- Soldering iron (optional, if cables need custom connectors)
- Heat shrink tubing or electrical tape for insulation
- Static wrist strap or ESD mat to protect electronics
Safety Tips
- Always power off your equipment before wiring or making adjustments.
- Use an anti-static wrist strap or work on an ESD-safe mat to avoid damaging sensitive driver electronics.
- Double-check power supply polarity before connecting—reversed polarity can fry the driver immediately.
- Keep wiring neat and secure to avoid shorts or accidental disconnects during operation.
Firmware Preparation and MODBUS-RTU Overview
Before powering up, ensure your firmware supports closed-loop stepper control and is configured for the MKS SERVO42D. Firmware like Klipper or Marlin can be set up for this driver, often using MODBUS-RTU commands to communicate settings like PID tuning and current limits over RS485 or CAN bus.
Taking time to prepare these essentials ensures a smooth, safe installation with less troubleshooting later. For a deeper dive into compatible PLC modules and communications protocols used in setups like this, you can explore related Siemens PLC modules that share communication standards similar to MODBUS-RTU.
Step-by-Step Physical Installation
Installing the MKS SERVO42D on your NEMA 17 motor is straightforward but requires precision for the best performance.
Mounting the SERVO42D on the NEMA 17 Base
- Align the driver to the motor base using the mounting holes on the SERVO42D board and corresponding holes on your NEMA 17 motor.
- Use proper screws—usually M3 or M4—to secure the driver firmly but avoid overtightening to prevent damage.
- Ensure the driver’s connectors face outward for easy wiring access.
Attaching and Aligning the Encoder Magnet
The encoder magnet is key for closed-loop feedback:
- Attach the magnet carefully to the motor shaft, typically on the flat part or the designated spot on the NEMA 17 shaft.
- Align it so the encoder sensor on the SERVO42D reads the magnet’s passes smoothly without wobble.
- Use a small gap (usually 1-2 mm) between the magnet and sensor for optimal readings.
- Spin the shaft by hand after mounting to check for stable encoder signals.
Heat Management Tips for Stable Operation
Servo drivers generate heat during use, so managing this is important:
- Mount the SERVO42D where there’s good airflow or add a small heatsink if necessary.
- Avoid enclosing the driver in tight, unventilated spaces.
- For long runs or high loads, consider active cooling like a fan.
- Monitor temperature during initial tests to prevent overheating, which can cause shutdowns or reduce performance.
Following these steps ensures your MKS SERVO42D and NEMA 17 motor work reliably and prepare the setup for smooth wiring and tuning ahead. For detailed wiring options and interface setup, check product info on MKS servo drivers and compatible motor setups.
Wiring Guide: Connections That Won’t Fry Your Setup
Proper wiring is critical to get your MKS SERVO42D running smoothly with your NEMA 17 motor without damaging anything. Here’s what you need to know:
Power Wiring and Polarity Checks
- Use the correct voltage recommended by the SERVO42D specs to avoid frying the driver.
- Double-check positive (+) and negative (−) terminals before powering up—reversed polarity is a quick way to ruin hardware.
- Always connect the power supply with the motor driver powered off for safety.
Motor and Encoder Wiring with Color-Coded Schematics
- Connect the NEMA 17 motor phases to the driver following the color codes: typically, A+/A− and B+/B− wires match the motor phases—refer to your motor’s datasheet.
- Attach the encoder wires carefully; most encoders have at least power (Vcc), ground, and two signal lines (A and B channels).
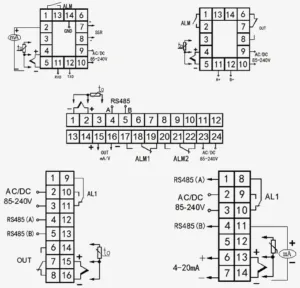
- Use the SERVO42D wiring diagram for exact pinouts—you can find detailed guides online or with the product manual.
Control Interface Options: Pulse Mode, RS485, CAN Bus
- The SERVO42D supports multiple control modes:
- Pulse mode uses pulse, direction, and enable pins—great for basic setups or upgrading existing stepper controls.
- RS485 interface allows MODBUS-RTU communication for advanced tuning and monitoring.
- CAN bus enables multi-driver synchronization and is ideal for scalable or complex machines.
- Choose the interface that best fits your firmware and control board capabilities.
Common Wiring Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Don’t mix up motor phases or encoder signals—wrong connections cause poor performance or no motion at all.
- Avoid long, unshielded cables for encoder signals to reduce electrical noise.
- Secure all connectors firmly to prevent loose contacts during operation.
- Always test connections with a multimeter before powering your system.
Taking these wiring steps seriously will save you headaches and keep your NEMA 17 servo upgrade running reliably. For a deeper dive into servo motor controls and joystick setups, review the detailed recommendations on servo motor usage at CNC Domi’s recommendations for choosing and using servo motors and joysticks.
Software Configuration and Tuning
Once your MKS SERVO42D is physically installed and wired correctly, it’s time to configure the software for optimal performance.
Power-On Checks and LED Status
When you power on the SERVO42D, pay close attention to the LED indicators. Each pattern signals different statuses:
- Solid green usually means normal operation.
- Blinking red or orange indicates errors like wiring issues or motor stalls.
- No light often means power or connection problems.
Consult your device manual for exact codes, but these LED signals will quickly help you troubleshoot basic issues.
Parameter Tuning: Microsteps, Current, and PID Values
Fine-tuning parameters is crucial:
- Microstepping: Adjust this to get smooth motor movement suited to your NEMA 17 motor. More microsteps mean quieter, precision motion but may reduce max speed.
- Current settings: Set the motor current to match your NEMA 17 specs—too high risks overheating, too low causes missed steps even with closed-loop.
- PID tuning: PID controls the servo loop accuracy. Start with default values and tweak based on torque and speed requirements, especially for CNC engraving or 3D printer applications.
Firmware Flashing and Integration with Klipper or Marlin
The MKS SERVO42D supports popular open-source firmware like Klipper and Marlin, making integration straightforward:
- Download the latest firmware version compatible with SERVO42D.
- Follow flashing procedures via USB or UART, using provided MODBUS RTU commands or firmware upload tools.
- Update configuration files to enable closed-loop mode, set microsteps, and adjust communication protocols (RS485 or CAN bus).
This enhances your printer or CNC’s step loss prevention and overall motion precision while providing quiet stepper motor operation.
Switching Between Open-Loop and Closed-Loop Modes
The SERVO42D can operate in both modes depending on your needs:
- Boucle ouverte: Similar to traditional stepper drivers, simpler but without feedback, suitable for basic setups.
- Boucle fermée: Uses encoder feedback for position correction, minimizing missed steps and improving print quality.
Switching modes usually involves firmware settings and sometimes hardware jumpers or dip switches on the driver board. Closed-loop mode is preferred for upgrades to silent NEMA 17 motors and robust CNC spindle control.
With the right tuning and firmware setup, your MKS SERVO42D will maximize your NEMA 17 motor’s efficiency and reliability, making your 3D printing or CNC work smoother and more precise.
For more professional grade controls and broader industrial applications, consider exploring drives like the Siemens SIMATIC S7-1200 digital output module, which offer enhanced automation options.
Testing and Calibration: Verify Your Install
Once your MKS SERVO42D is physically installed and wired, it’s crucial to test and calibrate to ensure everything runs smoothly.
- Basic Joystick and G-code Tests: Start by manually moving the motor using a joystick or simple G-code commands. This helps verify that wiring and firmware communication are solid. Watch for smooth, responsive motor movement without jitter or unexpected stops.
- Advanced Torque and Speed Calibration: Fine-tune the motor by adjusting parameters like current limits and PID values. This optimizes torque delivery and speed control, addressing common issues such as overheating or missed steps. Using the built-in diagnostic LEDs and your firmware’s feedback tools can make this process easier.
- Multi-driver Synchronization over CAN Bus: If you’re running multiple MKS SERVO42D drivers on a CAN bus network, check their synchronization closely. Proper syncing reduces step loss and torque inconsistencies, which is essential for multi-axis setups like 3D printers or CNC machines.
- Benchmarking Print or Cut Quality: After calibration, perform real-world tests like 3D printing a complex model or executing a CNC cut. Compare the results against previous setups with standard stepper drivers. You’ll often notice less noise, smoother motion, and improved precision, thanks to the closed-loop control and advanced tuning capabilities of the SERVO42D.
This step ensures your NEMA 17 motor upgrade not only works but performs at its best, minimizing surprises during operation. For detailed MODBUS-RTU command tuning and real-time diagnostics, check out resources on PLC motor control for streamlined troubleshooting and calibration.
Troubleshooting: Fix Issues Before They Stall Your Project
When working with the MKS SERVO42D servo driver for your NEMA 17 setup, troubleshooting quickly can save you a lot of downtime. Here are some common error messages and how to fix them:
- Motor not responding: Check motor wiring polarity and confirm the encoder cable is securely connected. Make sure power supply voltage matches driver specs.
- Encoder signal error: Re-align the encoder magnet and verify the encoder cable for damage or loose pins.
- Overcurrent or overheat warnings: Ensure proper heat dissipation—add cooling if needed—and double-check that motor current settings in firmware aren’t too high.
- Communication fault (RS485 or CAN bus): Verify bus wiring order and terminate resistors. Make sure device IDs and baud rates match your configuration.
To go deeper into diagnostics, use tools like the driver’s LED status codes and MODBUS-RTU command responses. These signals can tell you precisely where the problem lies—whether it’s wiring, micrologiciel, or motor issues.
Don’t hesitate to tap into community forums for shared fixes on the MKS SERVO42D or consult professional support if problems persist. Expert help can often speed up recovery, especially with complex CAN bus or PID tuning issues that require fine adjustments.
For advanced industrial-grade troubleshooting or upgrades, consider exploring high-quality servo amplifier options that support robust diagnostics and protection features tailored for demanding applications.
Advanced Applications and Upgrades with Doumi
The MKS SERVO42D isn’t just for upgrading your standard NEMA 17 motors—it’s perfect for advanced projects too. Par exemple, many users turn their Ender 3 into a much quieter, more precise machine by swapping out the original stepper drivers with this closed-loop servo solution. The results? Noticeably less noise and zero missed steps during printing.
Beyond 3D printers, the SERVO42D works great with CNC spindles and robotic arms where precise torque and smooth motion control are key. If you’re scaling up, Doumi also supports larger motors like NEMA 23 and specialized precision motor kits, offering the flexibility to match your project’s power and accuracy needs.
Looking ahead, firmware updates promise exciting features like AI-based tuning that will optimize PID settings automatically, as well as eco modes to reduce power consumption without sacrificing performance. For ease of use, Doumi bundles these drivers into plug-and-play kits, simplifying installation and setup for both hobbyists and professionals.
If you want to explore more on reliable motor control modules and advanced driver options, check out Doumi’s range of entraînements à fréquence variable (VFD) that complement sophisticated setups like the SERVO42D.