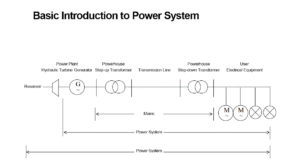
Blog
Servo Motor Guide How It Works Types Torque and Applications
If you’ve ever wondered what makes robots, drones, and precision machines move so smoothly and accurately, then understanding the servo motor is key. These compact devices play a crucial role in delivering precise control and feedback, powering everything from hobby projects to complex industrial automation. In this guide, we’ll break down exactly what a servo motor is, how it works, and why it’s the go-to choice for applications that demand accuracy and reliability. Ready to unlock the world of precise motion control? Let’s dive into everything you need to know about servo motors.
What Is a Servo Motor?
A servo motor is a special type of electric motor designed for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity, and acceleration. Unlike regular motors, servo motors can accurately move to a specific position and hold it, making them essential in applications where exact movement matters.
Core Definition and Purpose
- Purpose: To provide controlled motion with high precision and repeatability.
- Function: Converts electrical signals into mechanical motion with feedback for accuracy.
- Applications: Robotics, automation, RC vehicles, CNC machines, and more.
Brief History and Evolution
- Developed originally for military and aerospace systems where precise control was critical.
- Progressed from simple analog systems to advanced digital servos with microcontrollers.
- Now widely used in hobby electronics, industrial automation, and commercial devices.
Servo Motors vs. Other Motors
| Feature | Servo Motor | DC Motor | Stepper Motor | Brushless Motor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Closed-loop (feedback) | Open-loop | Open-loop | Usually open-loop or closed |
| Precision | High | Low | Moderate | High |
| Positioning | Accurate to precise angle | Continuous rotation | Fixed discrete steps | Precise with controllers |
| Torque at Low Speed | Strong | Varies | Moderate | Strong |
| Typical Use | Robotics, RC, CNC | Fans, simple drives | Printers, scanners | Drones, electric vehicles |
In , servo motors stand out because they combine precise position control with powerful, smooth motion—something DC, stepper, or brushless motors can’t fully achieve by themselves without additional control systems. This makes the servo motor the go-to option whenever you need dependable, accurate movement.
How Servo Motors Work
Servo motors operate using a closed-loop control system, which means they constantly monitor their position and adjust to match the command signals they receive. The core of this process relies on PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signals—short pulses where the width controls the motor’s angle or speed.
Here’s a simple breakdown of how it works:
- Signal Input: The motor receives a PWM signal from a controller, like an Arduino or RC transmitter. The length of the pulse dictates the target position.
- Position Feedback: Inside the servo, a feedback sensor (usually a potentiometer or encoder) measures the current position of the output shaft.
- Error Detection: The control circuit compares the current position to the target position from the PWM signal.
- Correction: If there’s a difference (called “error”), the servo motor adjusts its shaft to reduce the error, moving until it matches the commanded position.
- Continuous Loop: This feedback and correction cycle happens rapidly to maintain precise control.
This system allows servo motors to provide precise, smooth, and repeatable movement. It’s why they’re preferred over standard DC motors for applications requiring accuracy. The combination of closed-loop feedback and PWM control lets servos correct for load changes and mechanical resistance on the fly, maintaining exact positioning with minimal overshoot.
This closed-loop principle differentiates servo motors from other motors like stepper motors, which rely on open-loop step commands. Learn more about related industrial control systems at CNC Domi’s high-quality drives offerings designed for precision motion control.
Key Components of a Servo Motor
A servo motor consists of several essential parts that work together to provide precise control and movement:
- DC/AC Motor Core: This is the heart of the servo motor, generating the mechanical motion. Depending on the servo type, it can be a brushed DC motor, brushless DC motor, or an AC motor.
- Gearbox and Reduction Gears: These reduce the motor’s high speed to a slower, more manageable output speed while increasing torque. The gearbox is crucial for achieving fine control and powerful movement in applications.
- Position Feedback Sensor: Usually a potentiometer or an encoder, this sensor provides real-time position data to the control circuit. It enables the closed-loop feedback system, helping the motor know its exact shaft position and make precise adjustments.
- Control Circuit and Driver: This electronic system receives input signals (often PWM control servo signals) and interprets them to control the motor’s movement. It compares the desired position with the feedback signal to correct any position error automatically.
- Output Shaft and Horn: The output shaft is where the mechanical motion is delivered. Attachable horns or arms connect to the shaft, allowing the servo to move external parts such as wheels, levers, or robotic joints efficiently.
Understanding these components helps when selecting and troubleshooting servo motors, whether for hobby projects or industrial automation. For more on integrating motors with control systems, you might explore advanced automation drives like those seen in a Siemens servo system, which reflect similar core components scaled for industry use.
Types of Servo Motors
Servo motors come in various types, each designed to meet specific needs. The most common distinction is between hobby/RC servos and industrial servos. Hobby servos are small, affordable, and perfect for projects like remote-controlled cars, drones, or simple robotics. Industrial servos, on the other hand, are built tougher, offer higher precision, and handle more demanding tasks in manufacturing or automation.
There are also positional (standard) servos, which rotate typically up to 180°, used where precise angle control is needed. In contrast, continuous rotation servos can spin endlessly in either direction, useful for wheels or conveyor belts.
When it comes to motor types, AC servo motors are heavy-duty and used in industrial equipment due to their high efficiency and reliability. DC servo motors include both brushed and brushless types—the brushed versions are simpler and cheaper, while brushless DC motors offer greater durability and smoother operation.
Additionally, you’ll find specialty servos like linear servos, which provide straight-line motion instead of rotation, and high-torque servos made for applications requiring extra power.
For industrial-grade servo parts and drives, businesses often look to reliable suppliers like those offering Lenze servo motors, which combine performance and durability in tough environments.
Technical Specifications to Consider
When choosing a servo motor, understanding the key specs is a must. Here are the most important technical factors to keep in mind:
| Specification | What It Means | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Torque Rating | Measured in kg-cm or Newton-meters (Nm). Indicates the motor’s twisting force. | Determines the load the motor can handle without stalling. |
| Operating Voltage | The voltage range the servo can handle (usually 4.8V to 7.4V for hobby servos). | Matching voltage to your power supply ensures stable and safe operation. |
| Speed | Time taken to rotate 60° (e.g., 0.1 sec/60°). Fast speed means quicker response. | Important for applications needing fast motion, like robotics. |
| Rotation Range | Typical ranges: 180°, 360°, or multi-turn (several revolutions). | Choose based on whether precise positioning or continuous rotation is needed. |
| Stall Torque | Maximum torque before the motor stops moving. | Helps avoid overloading the motor and damaging gears or electronics. |
| No-Load Speed | Speed when the motor runs without any load. | Gives an idea of maximum responsiveness without stress. |
| Operating Temperature | The temperature range within which the servo runs safely. | Ensure durability, especially in harsh or outdoor environments. |
Your project’s success depends on selecting specs that fit your needs—overestimating means more cost and weight, underestimating risks failure.
For reliable choices tailored to different needs, check out sturdy industrial-grade options like the Fanuc servo motor series or learn more about specialized motor control with SEW Eurodrive motor control. Both are trusted in U.S. manufacturing and automation markets.
Common Applications of Servo Motors
Servo motors are everywhere in today’s tech-driven world thanks to their precision and reliability. Here’s where you’ll commonly find them:
- Robotics and Automation: Servo motors power robotic arms and automated assembly lines, delivering exact movements needed for tasks like welding, painting, or packaging.
- RC Vehicles, Drones, and Model Aircraft: Hobby servo motors control steering, throttle, and rudder movements, giving remote-controlled vehicles smooth and accurate handling.
- CNC Machines and Manufacturing: Industrial servo motors help control cutting tools and machinery in CNC devices, ensuring precise shaping and fabrication. For top quality servo motors suited for CNC use, check out reliable options like the Sanyo P50B08050DXS00 motor.
- Camera Systems, Antennas, and Medical Devices: Servo motors enable precise positioning for camera pan-tilt mechanisms, antenna tracking, and sensitive medical equipment adjustments.
- Everyday Uses: From automatic door openers to prosthetic limbs, servo motors offer smooth, controlled movements crucial for accessibility and convenience.
These varied applications highlight why selecting the right servo motor with proper torque and control features is essential for efficiency and performance in any project.
How to Choose the Right Servo Motor
Picking the right servo motor depends on a few key factors that match your project’s needs. Here’s a simple guide to help you decide:
| Factor | What to Consider | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Torque | How much force your project needs (kg-cm, Nm) | Too little torque means weak or stalled motion |
| Size & Weight | Space available for the motor and total weight | Fits properly and won’t overload your system |
| Power Supply | Operating voltage and current requirements | Must be compatible with your power source |
| Environment | Temperature range, moisture, dust exposure | Ensures motor longevity and reliability |
| Rotation Range | 180°, 360°, or multi-turn control | Depends on whether you need fixed or continuous rotation |
| Compatibility | Controller match, like Arduino or PLC | Easy integration and smooth control |
Matching Controllers: Arduino and More
If you’re using popular microcontrollers like Arduino, check for servo motors with good Arduino servo library compatibility. Many hobby servo motors are designed for easy plug-and-play with Arduino boards, making setup quicker and troubleshooting simpler.
DUOMI Recommendations for Your Project
DUOMI offers a range of reliable servo motors suited for both hobbyists and professionals. Whether you’re building a robot arm, an RC car, or CNC machinery, DUOMI’s lineup has options tailored to different torque ratings, sizes, and voltage requirements.
For advanced applications, consider servo motors matched with precise feedback devices or compatible control units like those found in DUOMI’s high-resolution encoder products or the Siemens motor controllers to ensure smooth and accurate movements.
By carefully balancing your project’s mechanical needs with power and control compatibility, you’ll find a servo motor that fits perfectly and performs reliably.
Controlling Servo Motors: Basics and Tips
Controlling a servo motor is straightforward but requires attention to wiring and power needs to get the best performance. Most servo motors run on 4.8 to 6 volts DC, so using a stable power supply or battery pack is key to avoiding issues like jitter or weak torque. Always connect the power ground and signal ground together to prevent signal interference.
When it comes to control, microcontrollers like Arduino are popular choices. Using an Arduino servo library simplifies sending PWM signals necessary for precise positioning or continuous rotation. The library handles the timing, so you only need to specify the desired angle or speed.
Common problems you might face include:
- Jittering: Usually caused by unstable power or noisy signal wiring. Using thicker wires and proper shielding can help.
- Overheating: Running a servo at or near stall torque for long periods overheats it. Make sure to size the servo correctly for your load.
- Weak torque: Could point to insufficient voltage or a faulty motor. Double-check your power source and wiring.
For reliable and high-quality servo motors, check products from trusted suppliers like DUOMI’s servo motor collection, where you’ll find models suited for both hobby projects and professional use.
Advantages and Limitations of Servo Motors
Servo motors are known for high precision and quick response times, making them ideal for tasks that require accurate positioning and smooth motion control. They also stand out for their energy efficiency, as they only draw the power they need to hold or move to a position. This means less wasted electricity compared to some other motor types.
However, servo motors come with some trade-offs. They tend to be more expensive and complex than simpler motors like basic DC or stepper motors, mainly because of the integrated feedback and control electronics. Also, most standard servo motors have a limited continuous rotation range—usually up to 180°—which can restrict their use in applications requiring full 360° constant rotation, though specialty continuous rotation servos are available.
Balancing these strengths and limitations is key when selecting a servo motor for your project or application. For instance, if you need precision but also full rotation, you might look for specific models or consider AC or brushless DC servo motors, which offer more flexibility.
For a reliable source of quality servo motors and controllers suited to various industrial and hobbyist needs, check out trusted Allen Bradley programmable logic controllers that pair well with servo systems.
DUOMI Servo Motor Recommendations
For those looking to choose reliable servo motors, DUOMI offers a solid lineup that suits both hobbyists and professionals. Their models strike a good balance between precision, power, and durability—ideal whether you’re working on a robotics project, CNC machine, or automation system.
Recommended DUOMI Servo Motors:
- DUOMI Standard Hobby Servo: Perfect for beginners and RC projects. It offers reliable torque and easy Arduino compatibility.
- DUOMI Industrial AC/DC Servos: Designed for high-performance applications with closed-loop feedback for precision control, great for manufacturing setups.
- DUOMI High-Torque Brushless Servos: These provide smooth, energy-efficient operation with longer lifespans, perfect for more demanding uses.
Integration Tips:
- Make sure to match the servo’s torque rating to your project needs—don’t underpower or over-size.
- Use proper drivers and controllers compatible with your servo type; DUOMI provides technical specs to help you find the right match.
- For DIY electronics, DUOMI servos work well with popular microcontrollers like Arduino using standard libraries.
Where to Buy:
DUOMI servo motors are widely available through authorized distributors and online retailers specializing in industrial automation parts. For reliable industrial-grade components, check out trusted suppliers with experience providing high-efficiency Siemens drives and genuine inverter replacements. This ensures you get quality and support for your automation projects.