Blog
Servo Motor Definition and Working Guide with Types and Applications
What Is a Servo Motor?
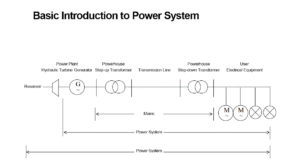
A servo motor is a specialized type of rotary or linear actuator that operates within a closed-loop control system. This means it uses continuous feedback to precisely control its position, speed, and torque. Unlike regular DC or AC motors that simply spin when powered, a servo motor adjusts its movement based on real-time feedback, making it ideal for applications where accurate and repeatable motion is essential.
The concept of servo motors dates back to early 20th-century engineering, initially developed for control systems in aviation and automation. Over time, advancements in electronics and control technology have refined servo motors into highly efficient and reliable devices used in everything from robotics to industrial machinery.
What makes a servo motor stand out from traditional motors is its feedback mechanism — usually via encoders or potentiometers — combined with a control circuit. This setup enables the motor to correct its position dynamically, offering greater accuracy and smoother performance compared to standard DC or AC motors, which run open-loop without position feedback. This precision is why servo motors are a go-to choice when exact control is critical, such as in CNC machines, drones, or robotic arms.
How Does a Servo Motor Work?
A servo motor works through a closed-loop system designed for precise control of position, speed, and torque. Here’s a simple step-by-step breakdown of the working principle:
- Input Signal: The servo receives a command signal, often a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal, which tells it the target position or speed.
- Motor Movement: The motor inside spins to adjust its shaft toward the desired position.
- Feedback: A position feedback device, like a potentiometer or encoder, constantly monitors the shaft’s actual position.
- Control Circuit: The control circuitry compares the current position to the target position and sends corrective signals to the motor if there’s a difference.
- Correction Loop: This feedback loop repeats continuously until the shaft reaches and holds the desired position.
The closed-loop feedback system is the heart of servo motor functionality—this allows it to self-correct in real-time, making it more precise and responsive than regular motors.
Role of PWM Signals
PWM signals control the motor by adjusting the width of pulses sent to the motor’s driver. The length of each pulse corresponds to the target position or speed, enabling extremely accurate control without wasting power. This method is key for servo motor efficiency and responsiveness in robotics, automation, and other applications.
Internal Components and Their Functions
Inside a typical servo motor, you’ll find:
- Motor: Can be DC, AC, or brushless, providing the force to rotate.
- Gear Train: Reduces speed and increases torque for finer control.
- Position Feedback Device: Like a potentiometer or encoder, feeds back real-time position data.
- Control Circuitry & Driver: Interprets input signals, processes feedback, and powers the motor accordingly.
Understanding how these parts work together helps explain why servo motors excel in tasks requiring precision and reliability.
For more tech insights related to industrial servo control, exploring components like the Fanuc CNC control system circuit board can provide deeper understanding of modern closed-loop control systems.
Main Components of a Servo Motor
A servo motor is made up of several key components that work together to provide precise control over position, speed, and torque. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Motor: This can be a DC motor, AC motor, or brushless motor depending on the application. Each type offers different performance benefits, with brushless motors often preferred for their efficiency and lower maintenance.
- Gear Train: The gear train amplifies the torque from the motor and reduces speed, allowing for smooth and powerful movements even in compact designs. This is crucial for applications requiring high torque at low speeds.
- Position Feedback Device: Accurate feedback is what sets servo motors apart. Common feedback devices include potentiometers, encoders, or resolvers. These sensors continuously monitor the motor’s position and send data back to the control system to ensure precision.
- Control Circuitry and Driver: The brain of the servo motor, the control circuitry interprets the input signals (like PWM control pulses) and adjusts the motor’s operation accordingly. The driver manages power delivery and ensures smooth, responsive control.
Together, these components create a closed-loop control system that’s essential for applications demanding accuracy and repeatability. For those interested in integrating high-efficiency drives and controllers with their servo motors, exploring options like DUOMI’s high-efficiency Siemens drive solutions can provide reliable performance boosts in industrial settings.
Types of Servo Motors
Servo motors come in various types, each suited for different tasks depending on power, precision, and control needs.
DC Servo Motors are common in applications requiring simple speed and position control. They use brushes and a commutator to deliver power, making them affordable but with some maintenance due to brush wear.
AC Servo Motors run on alternating current and excel in high-precision, high-speed applications. They are brushless, which means less maintenance and greater reliability, ideal for industrial automation and CNC machinery.
Brushless vs. Brushed Servo Motors – Brushless types offer higher efficiency, longer life, and smoother operation than brushed servo motors, which are simpler but wear out faster.
Positional Rotation vs. Continuous Rotation Servos define how far the servo shaft can move. Positional rotation servos move within a set angle (usually 0° to 180°), perfect for robotics joints or camera gimbals. Continuous rotation servos spin freely like a standard motor, used mainly in wheeled robots and conveyor belts.
RC/Hobby Servos vs. Industrial Servos differ in build quality and capability. RC servos are small, affordable, and designed for model cars, planes, drones, and hobby projects. Industrial servos are rugged, high-performance units built for precision manufacturing and heavy-duty automation. For example, reliable industrial-grade servo motors like the ones found in Fanuc driver systems offer robust control and longevity.
High-Torque Servo Motors deliver extra power for demanding applications like robotics arms, heavy machinery, or large automated systems. These servos often feature reinforced gears and larger motors to handle increased load without sacrificing precision.
Understanding these types helps you pick the right servo motor for your project, whether it’s a small RC car or a full-scale automated CNC setup.
Servo Motor vs. Stepper Motor: Key Differences
Servo motors and stepper motors might seem similar, but they serve different needs, especially when it comes to control type, precision, torque, speed, and cost. Here’s a quick breakdown:
| Feature | Servo Motor | Stepper Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Control Type | Closed-loop (feedback-based) | Open-loop (no feedback) |
| Precision | High, thanks to position feedback | Moderate, with fixed step angles |
| Torque | High torque at variable speeds | Good torque at low speeds |
| Speed | Fast and smooth rotation | Slower, with stepwise movement |
| Holding Capability | Strong holding torque with feedback | Limited holding torque |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | More affordable |
| Complexity | More complex electronics | Simpler control circuits |
| Typical Uses | Robotics, CNC, industrial automation | 3D printers, simple positioning, hobby projects |
When to Choose a Servo Motor
- You need precise control of position, speed, and torque.
- The application requires high speed or smooth motion.
- Holding torque is critical during operation.
- You can invest more in a control system with feedback.
When to Choose a Stepper Motor
- Your project is cost-sensitive.
- Positioning precision is needed but not ultra-high accuracy.
- Operation involves low-speed or simple repetitive movements.
- You prefer a simple open-loop control without feedback.
For advanced industrial setups, servo motors typically outperform stepper motors, especially with their feedback systems and dynamic response. If you want to explore servo systems, DUOMI offers a range of servo drive controllers designed for applications demanding precise closed-loop control.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Servo Motors
Servo motors offer several advantages that make them ideal for precise and dynamic control tasks:
- High precision: Thanks to their closed-loop feedback system, servo motors can accurately control position, speed, and torque.
- Efficiency: They deliver power efficiently, minimizing energy waste during operation.
- Fast dynamic response: Servo motors respond quickly to control signals, which is critical in robotics and automation.
- Reliable feedback accuracy: Using encoders or potentiometers, servo motors maintain consistent performance under varying loads.
However, there are some disadvantages to consider when choosing a servo motor:
- Higher cost: Due to their feedback devices and control circuitry, servo motors tend to be more expensive than standard motors or stepper motors.
- Complexity: The closed-loop system requires more sophisticated controllers and integration efforts.
- Power requirements: Servo motors often need more power supply capacity, especially high-torque models.
Knowing these pros and cons can help you decide if a servo motor fits your application—whether it’s an industrial machine, robotics system, or RC project. For detailed insights on maintaining servo motor performance, check out this practical servo motor preventive maintenance guide.
Common Applications of Servo Motors
Servo motors are everywhere when it comes to precise control and smooth motion. In robotics and automation, they’re the go-to choice for positioning arms, joints, and grippers with accuracy and speed. You’ll find robot servo motors running industrial robots on assembly lines, boosting productivity and precision.
In the world of RC vehicles, drones, and hobby projects, RC servo motors give you tight control over steering, throttle, and camera movement. Their compact size and quick response make them ideal for remote control planes, cars, and drones.
CNC machines and industrial manufacturing rely heavily on industrial servo motors to achieve repeatable, accurate tool positioning. These motors handle milling, cutting, and drilling tasks that demand high torque and exact feedback. For example, customers turning to DUOMI often equip their machines with Fanuc servo amplifiers to drive their servo motors seamlessly.
In the medical field, servo motors are key in devices like robotic surgery arms, imaging equipment, and automated drug dispensers. Meanwhile, cameras and antenna systems use them to adjust focus and alignment with smooth, silent motion.
DUOMI offers a solid range of servo motors, from high torque to RC and industrial types, tailored to these applications. Their products support precise motion control solutions, whether you’re working on a complex robot or a custom CNC setup.
How to Choose the Right Servo Motor
Selecting the right servo motor for your project depends on several key factors. Matching your application’s needs with the motor’s specifications ensures efficient, reliable performance.
Key Factors to Consider
| Factor | What to Check | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Torque | Required stall torque and continuous torque | Ensures the motor can handle the load without stalling |
| Speed | Maximum RPM and acceleration | Impacts how fast your system can respond |
| Size | Physical dimensions and weight | Fits the motor into your device or machine design |
| Voltage | Operating voltage range | Must match your power supply for safe operation |
| Environment | Temperature, humidity, and dust resistance | Affects motor durability and lifespan |
Important Specifications
- Stall Torque: The maximum torque the motor can hold without moving. Critical for load starting and holding.
- Operating Voltage: Confirm compatibility with your controller’s power output.
- Feedback Type: Choose between potentiometers, encoders, or resolvers based on precision needs.
Tips for Controller Integration
- Ensure your servo motor supports the control signals your device uses, such as PWM for hobby boards like Arduino or industrial protocols for PLCs.
- Confirm the motor driver or controller can handle the motor’s voltage and current ratings.
For industrial applications, you might explore advanced servo options like the Yaskawa inverter CIMR-G7A41P5, which offer robust control and compatibility with various motor types.
By focusing on these core aspects, you can confidently select a servo motor tailored to your project’s torque, speed, and environment requirements without overspending or running into compatibility issues.
DUOMI Servo Motors: Reliable Solutions for Your Projects
DUOMI offers a wide range of servo motors designed to meet the diverse needs of hobbyists, industrial users, and automation experts across the U.S. Whether you need a high-torque servo motor for heavy-duty machinery, a precise RC servo motor for your drone or robotic project, or rugged industrial servo motors for manufacturing automation, DUOMI has you covered.
Key Features and Benefits
- High Precision & Performance: DUOMI servo motors deliver accurate positioning and smooth motion, backed by advanced feedback systems and reliable closed-loop control.
- Variety of Types: From brushless DC servo motors to AC-driven options, all models come with integrated drivers and feedback devices for seamless integration.
- Durability: Built with robust materials and advanced gearing, suitable for demanding industrial environments or extended use in robotics.
- Easy Integration: Compatible with popular controllers like Arduino and PLCs, thanks to well-defined interfaces and industry-standard signals like PWM for precise speed and position control.
Real-World Use Cases
Several users have successfully integrated DUOMI servo motors into robotic arms, CNC machines, and automated packaging lines. For example, precision-driven industrial servo motors paired with Fanuc servo amplifier units provide superior performance in automated manufacturing cells. Meanwhile, hobbyists enjoy the smooth response and reliability of DUOMI’s RC servo motors in drones and remote-controlled cars.
Choosing DUOMI means investing in trusted, high-quality servo solutions built to power your projects with accuracy and durability. Whether it’s robotic automation or hobbyist creations, DUOMI servo motors ensure reliable control and lasting performance.